Cosmetic Gums Surgery
Cosmetic Gums Surgery
Cosmetic gum surgery, also known as periodontal plastic surgery or gum contouring, refers to a range of procedures aimed at improving the appearance of your gums and enhancing your smile. These procedures address various aesthetic concerns related to gum tissue, such as excessive gum display (gummy smile), uneven gum line, or insufficient gum tissue.
Reasons for Cosmetic Gum Surgery:
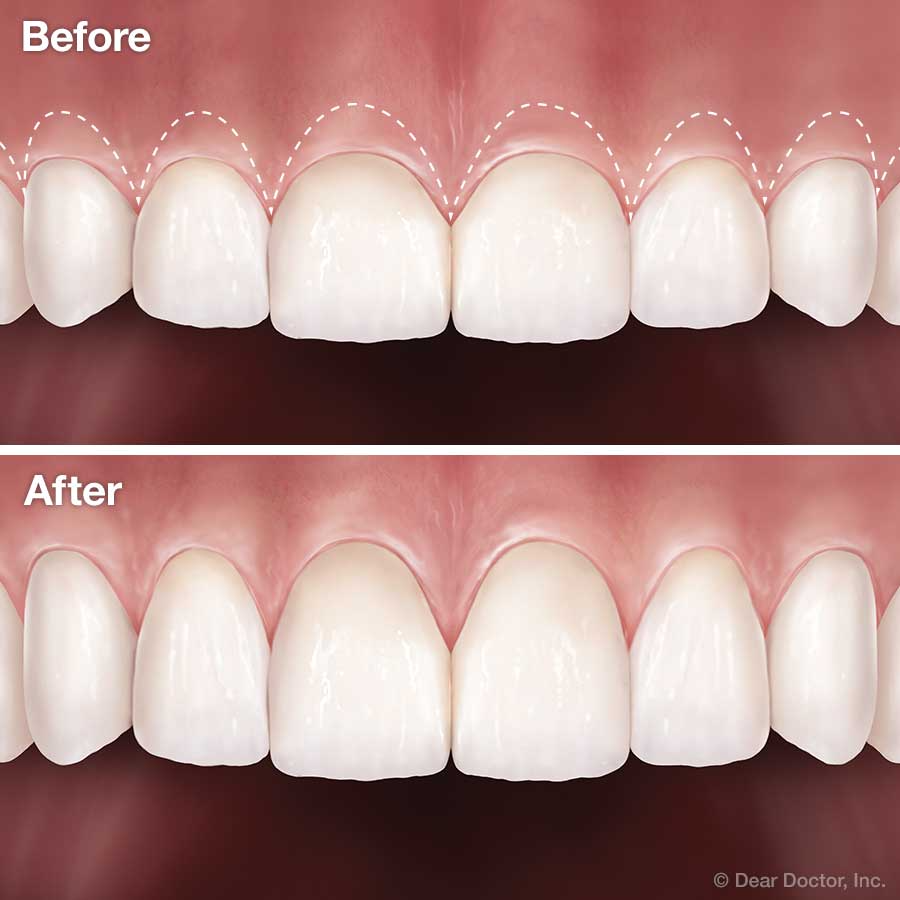
- Gummy Smile (Excessive Gingival Display): This is one of the most common reasons. Too much gum tissue showing when you smile can make teeth appear short.
- Uneven Gum Line: An asymmetrical gum line can make teeth look uneven in length, even if the teeth themselves are properly shaped.
- Receding Gums: While gum recession is often a result of gum disease, in some cases, it can be addressed cosmetically to improve the appearance of the teeth and prevent further recession.
- Short Clinical Crowns: When teeth appear short due to excessive gum tissue covering them, crown lengthening can expose more of the tooth surface.
- Black Triangles: These are the dark spaces that can appear between teeth near the gum line, often due to gum recession or the shape of the teeth.
- Ridge Augmentation: After tooth loss, the underlying bone and gum ridge can collapse. Ridge augmentation procedures can restore the natural contour of the gums for a more aesthetic appearance, especially when considering dental implants or bridges.
Types of Cosmetic Gum Surgery Procedures:
- Gingivectomy (Gum Contouring): This procedure involves surgically removing excess gum tissue to expose more of the tooth crown, making the teeth appear longer and reducing a gummy smile. It can also be used to create a more even gum line.
- Gingivoplasty: This procedure reshapes healthy gum tissue to improve its appearance. It’s often performed in conjunction with a gingivectomy to refine the gum line and create a more natural contour around the teeth.
- Crown Lengthening: While sometimes necessary for restorative purposes (e.g., placing a crown on a tooth with insufficient structure), crown lengthening can also be cosmetic. It involves removing gum tissue and sometimes underlying bone to expose more of the tooth’s surface, making short teeth appear longer.
- Gum Grafting: This procedure involves taking gum tissue from another area of the mouth (usually the palate) or using donor tissue to cover exposed tooth roots due to gum recession. This can improve aesthetics, reduce sensitivity, and protect the tooth from further damage.
- Frenectomy/Frenotomy: These procedures involve releasing or removing a tight or abnormally attached frenum (a small fold of tissue) in the mouth. A labial frenum that attaches too close to the gum line between the upper front teeth can cause a gap or contribute to gum recession.
- Ridge Augmentation: This procedure rebuilds or reshapes the alveolar ridge (the bony ridge in the jaw that supports teeth) after tooth loss. It often involves bone grafting and soft tissue manipulation to create a more natural contour for future tooth replacement or simply to improve aesthetics.
- Papilla Reconstruction: This aims to restore or rebuild the interdental papillae (the triangular gum tissue between teeth) that may have been lost due to gum disease, trauma, or tooth shape. This can eliminate black triangles and improve the overall appearance of the gum line.
The Cosmetic Gum Surgery Procedure:
The specific steps involved depend on the type of surgery being performed. However, a general outline includes:
1. Consultation and Examination: The dentist or periodontist will thoroughly examine your gums and teeth, discuss your aesthetic goals, and determine the most appropriate treatment plan. This may involve X-rays and impressions.
2. Anesthesia: Local anesthesia is typically administered to numb the area being treated. Sedation options may be available for patients with anxiety.
3. Surgical Procedure: The surgeon will use specialized instruments, lasers, or electrosurgery to remove, reshape, or graft gum tissue according to the treatment plan.
4. Suturing (if necessary): In many cases, sutures (stitches) will be placed to help the tissues heal properly. These are usually removed after a week or two.
5. Post-operative Instructions: You will receive detailed instructions on how to care for the surgical site, manage pain, and maintain oral hygiene during the healing period.
Recovery After Cosmetic Gum Surgery:
Recovery time varies depending on the extent of the surgery. Common post-operative instructions include:
- Pain Management: Taking prescribed or over-the-counter pain medication.
- Cold Compresses: Applying ice packs to reduce swelling.
- Soft Diet: Eating soft foods to avoid irritating the surgical site.
- Gentle Oral Hygiene: Carefully cleaning the untreated areas of your mouth and avoiding brushing directly on the surgical site initially. You may be instructed to use a special mouthwash.
- Rest: Avoiding strenuous activity.
- Follow-up Appointments: Attending all scheduled follow-up appointments with your dentist or periodontist to monitor healing.
Benefits of Cosmetic Gum Surgery:
- Improved Smile Aesthetics: Creates a more balanced and attractive smile.
- Enhanced Confidence: Addressing aesthetic concerns can boost self-esteem.
- More Even Gum Line: Makes teeth appear more uniform in length.
- Reduced Gummy Smile: Exposes more of the natural tooth structure.
- Coverage of Exposed Roots: Reduces sensitivity and protects teeth from further damage.
- Improved Oral Health (in some cases): Gum grafting can prevent further recession, and crown lengthening can facilitate better restorative work.
- Preparation for Other Cosmetic Procedures: Can create a more ideal foundation for veneers or crowns.
Book your Appointment Today!
Your smile is just one click away.
